Camera Calibration and Rectification
Last updated on November 26, 2023 pm
[TOC]
Overview
LIBCBDETECT: Corner and Checkerboard Detection: MATLAB code for fully automatic sub-pixel checkerboard / chessboard pattern detection

What Calib Do
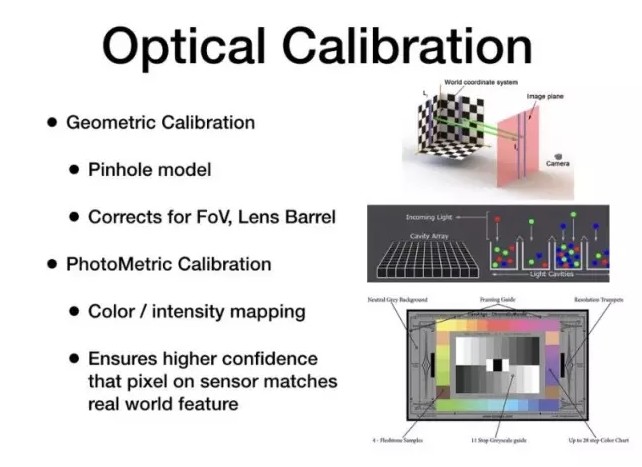
Camera calibration is the process of estimating intrinsic and/or extrinsic parameters.
- Intrinsic parameters deal with the camera's internal characteristics, such as, its focal length, skew, distortion, and image center.
- Extrinsic parameters describe its position and orientation in the world
When To Calib
Your camera might be out of calibration if you had the following symptoms: * Reduced depth density on objects in the operating range (might still get some depth). * Flat surfaces look "wobbly", i.e. there is more deviation from the flatness than usual. * Measuring the physical distance to objects are not within expected range.
How To Calib
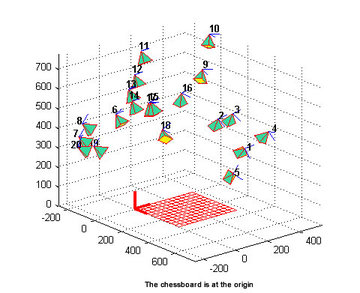
Calibration Placement
- from boofcv
- from ros

Calibration Best Practices
- Choose the right size calibration target
- Perform calibration at the approximate working distance (WD) of your final application
- Use good lighting
- normal lighting conditions from general office lighting (around 200 LUX) to more brighter lighting with additional floor lamp (around 1000 LUX)
- The lighting on the chart should be generally uniform without hotspots
- Use diffuse lighting, a spotlight will make the calibration target much more difficult to detect
- Collect images from different areas and tilts
- Have enough observations (at least 6 observations)
- Consider using CharuCo boards
- Calibration is only as accurate as the calibration target used
- Proper mounting of calibration target and camera
- the target needs to be mounted on a flat surface. Any warping will decrease calibration accuracy. An ideal surface will be rigid and smooth.
- Remove bad observations
OpenCV
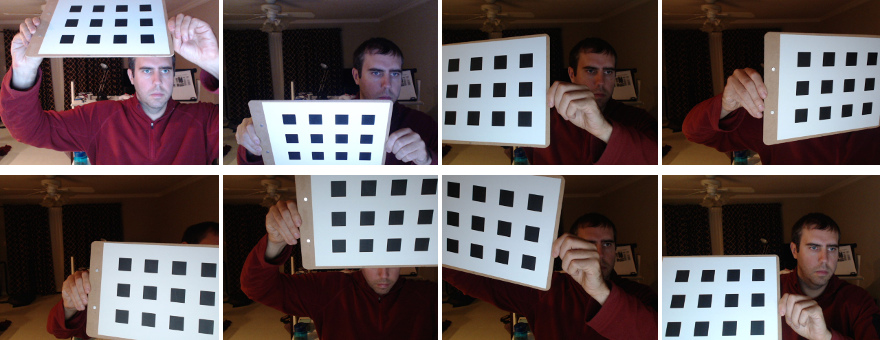
Basically, you need to take snapshots of these patterns with your
camera and let OpenCV find them.
Each found pattern results in a new equation.
To solve the equation you need at least a predetermined number of
pattern snapshots to form a well-posed equation system.
This number is higher for the chessboard pattern and less for the circle
ones.
For example, in theory the chessboard pattern requires at least two
snapshots.
However, in practice we have a good amount of noise present in our input
images, so for good results you will probably need at least 10 good
snapshots of the input pattern in different positions.
Calibration Patterns
- https://calib.io/
- Calibration targets (Kalibr)
- Camera Calibration Targets (boofcv)
- 机器视觉标定板
- Intel® RealSense™ D400 Camera OEM Calibration Target
Pattern size
As a rule of thumb, the calibration plate should have an area of at least half the available pixel area when observed frontally
Pattern type
Checkerboard or Chessboard
- their corners are simple to detect and "mostly" invariant to lens distortion
- its hard get right next to the image border, but you can get close
Square Grids
- allow you to get right up next to the image border
- It's more complex for a library developer to write a good high precision unbiased corner.
Circle Grids
- Circle Hexagonal Grid
- works well for regular camera lenses but is typically less accurate than chessboard of square grid because their features can't be measured directly
- Tangent points are invariant under perspective distortion
- Sometimes a library will use the center point, but this is ill advised because it's not invariant under perspective distortion
- Errors introduced by lens distortion are less significant when the circles are small inside the image, but under heavy lens distortion these are a poor choice
- Circle Regular Grid
- have essentially the same pros/cons as circle hexagonal but don't have the same circle density
ChArUCo: Chessboard + ArUco

ArUco vs Chessboard
- ArUco markers and boards
- fast detection and their versatility
- the accuracy of their corner positions is not too high, even after applying subpixel refinement
- Chessboard patterns
- the corners of chessboard patterns can be refined more accurately since each corner is surrounded by two black squares
- finding a chessboard pattern is not as versatile as finding an ArUco board
Calibration with ChArUco Boards and ArUco Boards
As it can be stated, calibration can be done using both, marker corners or ChArUco corners. However, it is highly recommended using the ChArUco corners approach since the provided corners are much more accurate in comparison to the marker corners. Calibration using a standard Board should only be employed in those scenarios where the ChArUco boards cannot be employed because of any kind of restriction.
AprilTag Grid

Calibration Quality Check
Quick Check
- if straight edges are straight
- Point the camera to a flat surface such as a wall about 1 to 2 meters away (3 to 6 feet) and avoid black surfaces. Visually inspect the depth image display of the wall. A lot of black dots or holes on the image is an indication of the camera being out of calibration.
- For stereo images you can see if rectification is correct by clicking on an easily recognizable feature and seeing if it is at the same y-coordinate in the other image.
Accuracy Check
This procedure should be used to check the accuracy of the camera.
- Reprojection error statistic
- Qualitatively speaking, a good calibration yields +- 1px reprojection error
- Calibrate the camera with the ATAN model and make sure you have a very low reprojection error (~0.1px) (from SVO)
- For a well made target and a decent camera reprojection error is typically around 0.1 pixels
- Typically, an epipolar error below 0.25 pixel is considered acceptable, and below 0.1 excellent (from ROS StereoCalibration)
- Expect accuracy within 2% at @2 meters
- Place the camera in parallel to a flat wall and exactly two meter (2000 mm) away. Once the camera is placed in its position, Use Intel® RealSenseTMViewer or Depth Quality Tool to measure the absolute distance. For a flat surface at a distance of 2 meter the absolute distance should be within 2% or better at 2 meter (2000mm). If the distance is not within the defined range, then the camera needs to be calibrated.
Rectification
Stereo Rectification
Stereo rectification is the process of distorting two images such that both their epipoles are at infinity, typically along the x-axis. When this happens the epipolar lines are all parallel to each other simplifying the problem of finding feature correspondences to searching along the image axis. Many stereo algorithms require images to be rectified first.
Calibration & Rectification Utils
OpenCV
- Interactive camera calibration application
- Calibrate fisheye lens using OpenCV
- Omnidirectional Cameara Calibration
- Custom Calibration Pattern for 3D reconstruction
camera_calibration (ROS Wiki)
- http://wiki.ros.org/camera_calibration
Supported camera model: pinhole camera model, which is standard in OpenCV and ROS
Matlab
Caltech's Camera Calibration Toolbox for Matlab (by Jean-Yves Bouguet)
- http://www.vision.caltech.edu/bouguetj/calib_doc/
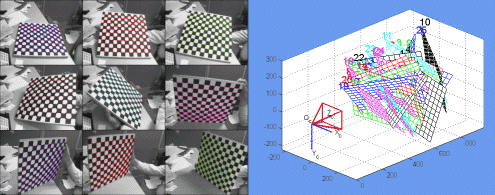
Omnidirectional Calibration Toolbox (by Christopher Mei)
- The toolbox has been successfully used to calibrate hyperbolic, parabolic, folded mirror, spherical and wide-angle sensors.
- It is a combination of the unified projection model from Geyer and Barreto and a radial distortion function. This model makes it possible take into account the distortion introduced by telecentric lenses (for parabolic mirrors) and gives a greater flexibility (spherical mirrors can be calibrated).
OCamCalib: Omnidirectional Camera Calibration Toolbox for Matlab (by Davide Scaramuzza)
- https://sites.google.com/site/scarabotix/ocamcalib-toolbox
- Omnidirectional Camera Calibration Toolbox for Matlab (for Windows, MacOS & Linux)
- For catadioptric and fisheye cameras up to 195 degrees
Improved OcamCalib
- urbste/ImprovedOcamCalib: an add-on to the OCamCalib toolbox by Scaramuzza et al.
Camera Calibration Toolbox for Generic Lenses (by Juho Kannala)
- http://www.ee.oulu.fi/~jkannala/calibration/calibration.html
This is a camera calibration toolbox for Matlab which can be used for calibrating several different kinds of central cameras. A central camera is a camera which has a single effective viewpoint. The toolbox has been successfully used for both conventional and omnidirectional cameras such as fish-eye lens cameras and catadioptric cameras.
Calibr
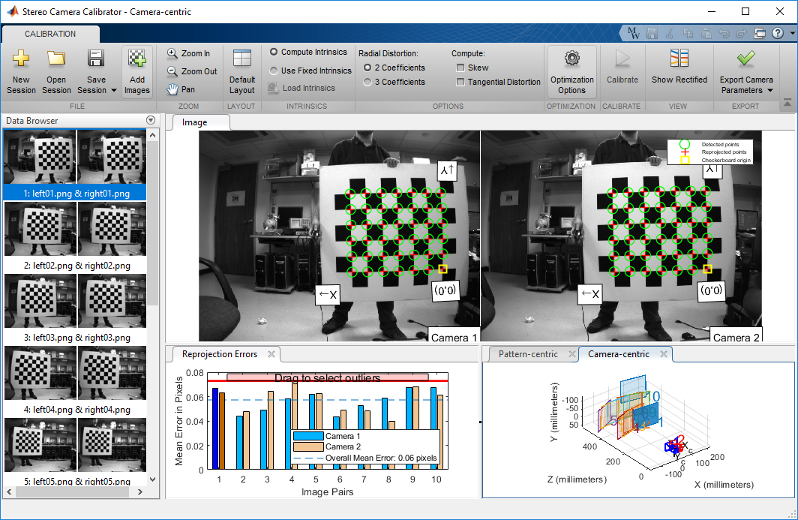
Stereo Camera Calibrator App
- https://www.mathworks.com/help/vision/ug/stereo-camera-calibrator-app.html
SWARD Camera Calibration Toolbox
- http://swardtoolbox.github.io/
Matlab code for Super-Wide-Angle-lens Radial Distortion correction just using a single image of a checkerboard
CamOdoCal
- https://github.com/hengli/camodocal
Automatic Intrinsic and Extrinsic Calibration of a Rig with Multiple Generic Cameras and Odometry.
This C++ library supports the following tasks:
* Intrinsic calibration of a generic camera.
* Extrinsic self-calibration of a multi-camera rig for which odometry
data is provided.
* Extrinsic infrastructure-based calibration of a multi-camera rig for
which a map generated from task 2 is provided.
The intrinsic calibration process computes the parameters for one of the following three camera models:
- Pinhole camera model
- Unified projection model (C. Mei, and P. Rives, Single View Point Omnidirectional Camera Calibration from Planar Grids, ICRA 2007)
- Equidistant fish-eye model (J. Kannala, and S. Brandt, A Generic Camera Model and Calibration Method for Conventional, Wide-Angle, and Fish-Eye Lenses, PAMI 2006)
By default, the unified projection model is used since this model approximates a wide range of cameras from normal cameras to catadioptric cameras. Note that in our equidistant fish-eye model, we use 8 parameters: k2, k3, k4, k5, mu, mv, u0, v0. k1 is set to 1.
GML C++ Camera Calibration Toolbox
GML Camera Calibration toolbox is a free functionally completed tool for cameras' calibrating. You can easy calculate intrinsic and extrinsic camera parameters after calibrating.
EasyCal Toolbox
- The EasyCal Toolbox can be used to calibrate a large cluster of cameras easily eliminating the need to click tediously on multiple images.
Image Rectification Utils
- image_proc (ROS wiki)
- Single image rectification and color processing.
- ethz-asl/image_undistort
- A compact package for undistorting images directly from kalibr calibration files, Can also perform dense stereo estimation